Exploring the World of Auto Mechanic Careers: Training and Certification
Auto mechanics play a crucial role in keeping vehicles running smoothly and safely on the roads. For those interested in pursuing a career in this field, understanding the training requirements, certification processes, and job prospects is essential. This article delves into the world of auto mechanic careers, focusing on work-and-learn opportunities, training programs, and the path to certification and licensing.
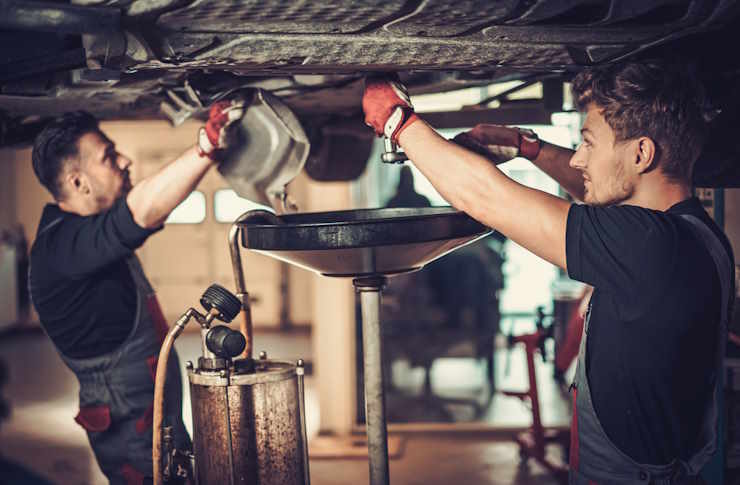

What does an auto mechanic do on a daily basis?
Auto mechanics, also known as automotive service technicians, perform a wide range of tasks to diagnose, maintain, and repair vehicles. Their daily responsibilities may include:
-
Conducting routine maintenance such as oil changes, tire rotations, and brake inspections
-
Diagnosing complex mechanical issues using computerized diagnostic equipment
-
Repairing or replacing faulty components, including engines, transmissions, and electrical systems
-
Performing state vehicle inspections and emissions tests
-
Communicating with customers about vehicle issues and repair recommendations
As vehicles become increasingly complex with advanced technology, auto mechanics must continuously update their skills to keep pace with the evolving industry.
How can I start a career as an auto mechanic?
Starting a career as an auto mechanic typically involves a combination of education and hands-on experience. Here are some steps to begin your journey:
-
Complete high school or obtain a GED, focusing on courses in math, physics, and computer science
-
Enroll in a vocational program or community college offering automotive technology courses
-
Gain practical experience through internships or entry-level positions at auto repair shops
-
Consider pursuing certifications from organizations like the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE)
-
Stay updated on the latest automotive technologies through ongoing training and workshops
Many aspiring mechanics also find success through work-and-learn programs, which combine on-the-job training with formal education.
What are work-and-learn auto mechanic programs?
Work-and-learn auto mechanic programs offer a unique approach to training, allowing students to gain practical experience while simultaneously receiving formal education. These programs often involve:
-
Alternating periods of classroom instruction and hands-on work experience
-
Partnerships between educational institutions and automotive employers
-
Opportunities to earn wages while learning
-
Exposure to a variety of vehicle types and repair scenarios
-
Mentorship from experienced mechanics
These programs provide a valuable pathway for aspiring mechanics to develop their skills, build professional networks, and potentially secure full-time employment upon completion.
What does auto mechanic training typically involve?
Auto mechanic training programs are designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of vehicle systems and repair techniques. Common components of these programs include:
-
Classroom instruction on automotive theory and principles
-
Hands-on practice in workshop settings
-
Training on diagnostic equipment and computerized systems
-
Courses on specific vehicle components (e.g., engines, transmissions, electrical systems)
-
Safety procedures and workplace regulations
Many programs also incorporate specialized training for hybrid and electric vehicles, reflecting the industry’s shift towards more sustainable transportation options.
What certifications and licenses do auto mechanics need?
Certification and licensing requirements for auto mechanics can vary by location and employer. However, obtaining certain credentials can significantly enhance job prospects and earning potential. Here are some key certifications and licenses:
-
ASE Certification: Offered by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence, these certifications cover various specialties and are widely recognized in the industry.
-
Manufacturer-Specific Certifications: Many automakers offer specialized training and certification programs for their vehicle brands.
-
State Licenses: Some states require auto mechanics to obtain a license, which may involve passing an exam and meeting specific educational or experience requirements.
-
EPA Section 609 Certification: Required for mechanics working with automotive refrigerants.
-
Continuing Education: Many certifications require ongoing training to maintain credentials and stay current with industry advancements.
How much can I expect to earn as an auto mechanic?
The earning potential for auto mechanics can vary based on factors such as experience, location, specialization, and certifications. Here’s a general overview of salary expectations:
| Experience Level | Median Annual Salary | Salary Range |
|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level | $35,000 | $25,000 - $45,000 |
| Mid-Career | $45,000 | $35,000 - $60,000 |
| Experienced | $60,000 | $45,000 - $75,000 |
| Master Mechanic | $75,000+ | $60,000 - $100,000+ |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Factors that can influence an auto mechanic’s earnings include:
-
Specialization in high-demand areas (e.g., electric vehicles, luxury brands)
-
Advanced certifications and ongoing training
-
Geographic location and local market conditions
-
Type of employer (e.g., dealership, independent shop, fleet service)
In conclusion, a career as an auto mechanic offers diverse opportunities for those passionate about vehicles and problem-solving. By pursuing comprehensive training, obtaining relevant certifications, and staying abreast of industry advancements, aspiring mechanics can build rewarding and stable careers in this essential field.